The European Air Traffic Management system is undergoing a profound transformation to make air transport more sustainable, smart and resilient to unplanned events, enabling new aircraft and vehicles - such as drones, balloons and satellites - to fly in conventional and non-conventional airspaces.
Technological progress in broadband connectivity, cloud computing, automation and artificial intelligence is at the core of this transformation, due to their maturity and affordable implementation costs. The digitalisation process is, however, taking much longer in aviation than in other businesses. This is due to the importance of safety aspects and the characterisation of aviation as a network industry in which capital-intensive investments from a range of stakeholders have to be synchronised around the same standards.
ALG has been actively participating in this exciting and challenging process for the last 15 years. It is a trusted advisor to the European Commission, EUROCONTROL, EASA, EDA, EUSPA and ESA, and is involved in a number of key innovation projects, such as SESAR and the EASA Data 4 Safety programmes to contribute to the digital transformation of aviation from its foundations.
Objectives, goals and purposes
Our objective is to ensure best-in-class support for projects spanning the whole innovation life cycle, from exploratory research to industrial research and validation of the solutions, through to implementation. The only way this can be achieved is through comprehensive expertise, provided by teams of ALG consultants, ensuring a holistic approach in dealing with the many facets of each project, including:
- Technical expertise, to guarantee, through an engineering approach, that all technological innovation is tailored to supporting people efficiently throughout their journeys by air in safety, including airport operations, airspace design and management, and air traffic management.
- The regulatory framework, including application of European and national policies and regulations from parliament, the EASA and national Civil Aviation Authorities, applying the most effective and balanced approach.
- The business aspect, including analysis of market, economic and financial mechanisms, through cost-benefit analysis and business cases, to ensure the sustainability of this transformation for the actors involved and to incentivise change.
- Project management, by establishing a Programme Management Office with the right plans, tools and methodologies to ensure that the implementation of the innovation is safe, efficient and controlled, to ensure business continuity at all time.
Study methodology and activities
All projects are unique, but ALG’s approach is always to tackle them in the same way: understand the problem, analyse possible solutions and plan implementation. Major programmes include:
- The SESAR programme: ALG has been contributing to various work streams since the inception of the development programme in 2010, particularly:
● The European ATM Master Planning, in which ALG is focusing on the business aspect of the SESAR deployment scenarios, ensuring their coherency and added value with respect to the baseline and reference scenarios.
● Performance assessment of the SESAR solutions, mainly though simulation software and analytical models, describing performance dynamics and key indicators fed with accurate historical operational data.
● The European ATM architecture, where we are taking care of the engineering aspect and description of the SESAR solutions, which together form the blueprint for the Digital European Sky.
● The Operational Service and Environment Description (OSED), through definition of the operational requirements of the SESAR solution in support of the development work and validation exercises.
● The SESAR deployment, where we are supporting clients in obtaining and managing European funds for the implementation of SESAR Solutions. - The EUROCONTROL iNM Programme: ALG has played a key role in integrated network management (iNM) since its inception. ALG is supporting execution of the programme working hand-in-hand with Indra, mainly through:
● Membership of the governance board leading programme, business and delivery aspects.
● Leading development and maintenance of the Digital Products Roadmap, inheriting the future business developments in NM and planning their delivery through successive releases of new services and functionality.
● Supporting performance of the programme by maintaining the Work Plan, managing dependencies and assessing commercial implications.
● Being a core contributor to the Project Management Office enabling the teams to work in an efficient and coordinated manner and ensuring they always use the right tools, methodologies, standards, programme knowledge and processes in their work.
Key findings and recommendations
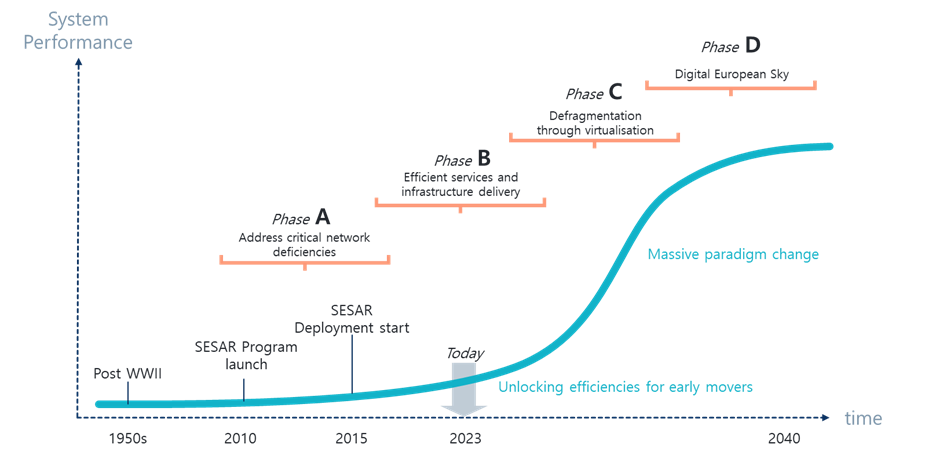
Innovation is always challenging due to the uncertainty of the unknown and the difficulty of changing established processes and habits in people and organisations. This complexity is magnified in the digital transformation of air traffic management, due to the criticality of systems and procedures for safety. This requires years of research, validation and assessment before implementation. The S-curve for adoption of innovation (Foster, 1985) is well suited to this context. The four progressive and overlapping phases identified in the European ATM Master Plan for ATM digitalisation bring increasing performance improvements at the local and network levels. This is illustrated in the diagram below.
Success and outcomes
Thirteen years after the launch of the SESAR Programme, the digital transformation of European ATM is now becoming tangible.
The successful solutions that have completed the innovation process, from R&D to validation through a regulatory mandate under EU Regulations 409/2013 and 2021/116, include:
- Free Route Airspace (FRA): under the legacy network structure, aircraft used to fly an average of 20 km further than the most direct route between two points. The FRA solution is a step forward in operational efficiency and environmental sustainability, offering more direct route options for flight planning on a large scale, covering increasingly large volumes of airspace. This solution has now been successfully implemented all over Europe, for both intranational and international options, reducing the nautical miles flown per year by approximately 2%. ALG was responsible for the cost benefit analysis of “Free Routing in high and very high complexity environments” in SESAR PJ.06-01.
- Remote Towers: a new solution enabling air traffic controllers to provide services to aircraft from a remote location through visual reproduction of the airfield on out-of-the-windows-view displays, augmented with digital capabilities, such as infrared cameras for night vision and pan-tilt-zoom cameras for binocular views. The world’s largest remote tower centre was opened in Bodø in Norway in 2022. This will initially control fifteen towers at fifteen airports remotely. Remote towers can reduce initial capital investment by 30%-40% compared to concrete towers, and operating costs by about 20%. ALG has been supporting technology suppliers, air navigation service providers and civil aviation authorities around the world with business and technical assessment prior to investment decisions.
- Total Airport Management: a concept that takes a holistic view of airport operations, including all key processes and the interactions between them, as the degree of synchronisation between these processes is a significant contributory factor to punctual and predictable operations and, ultimately, passenger satisfaction. ALG is contributing to SESAR PJ.04 W2 by defining the Operational Service and Environment Definition (OSED) and developing the solution architecture and modelling in European ATM Architecture (EATMA).
We expect that a wide range of solutions will be implemented in the next few years, consolidating performance improvements at the local level and starting to introduce benefits at the network level, where most of the performance envelope still needs to be unveiled.

